Eden Island Hurghada Booking – Your Complete Guide to Paradise 2026
Eden Island Hurghada Booking – Book Your Dream Red Sea Escape with HurghadaToGo
When it comes to luxury sea excursions in Hurghada, few places can match the beauty, serenity, and exclusivity of Eden Island Hurghada. This tropical paradise, nestled in the heart of the Red Sea, offers visitors a perfect mix of crystal-clear waters, soft sandy beaches, and vibrant marine life. With HurghadaToGo, you can easily book your unforgettable Eden Island experience, complete with seamless transfers, professional service, and memories that will last a lifetime.
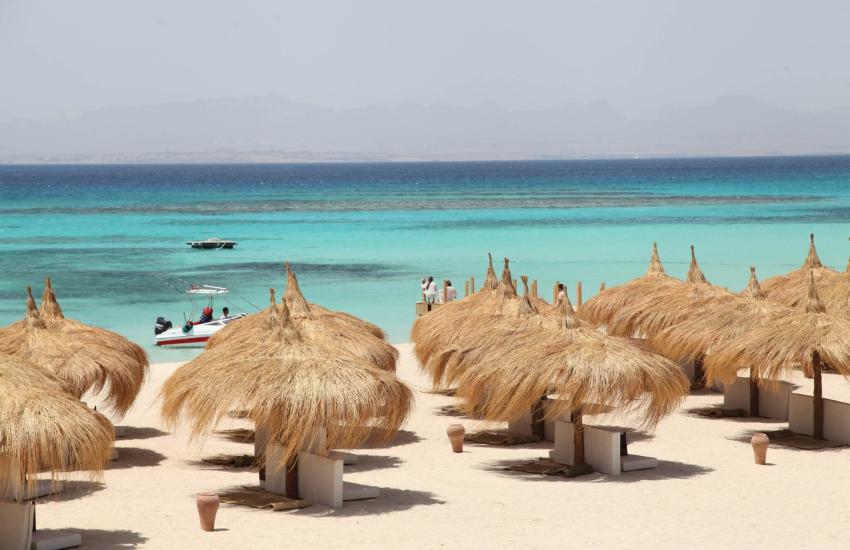

Why Choose Eden Island Hurghada?
Eden Island is more than just a day trip — it’s an escape to a private slice of heaven. Located just a short boat ride from Hurghada, the island offers:
Pristine white sandy beaches perfect for sunbathing and relaxation.
Turquoise waters ideal for snorkeling, swimming, or simply floating peacefully.
Rich marine life including colorful coral reefs and tropical fish.
Exclusive ambiance far away from the crowds, giving you the chance to enjoy tranquility.
Whether you’re looking for a romantic getaway, a fun family adventure, or a luxurious holiday highlight, Eden Island ticks every box.
Your Eden Island Trip with HurghadaToGo
Booking with HurghadaToGo ensures that your experience is smooth from start to finish. Here’s what you can expect:
Hotel Pickup & Transfer – Comfortable air-conditioned transport directly from your hotel in Hurghada, El Gouna, Makadi Bay, or Sahl Hasheesh.
Boat Ride to Eden Island – Relax and enjoy the views as you cruise across the Red Sea to reach the island.
Welcome to Eden – Step onto the soft sandy beach and take in the stunning scenery.
Snorkeling & Swimming – Explore coral reefs, swim in crystal-clear waters, or simply unwind on the beach.
Lunch & Refreshments – A delicious meal and soft drinks are included to keep you energized during your island adventure.
Free Time to Relax – Sunbathe, snorkel, or enjoy a peaceful walk along the shore.
Return Transfer – End your trip with a smooth ride back to your hotel, full of memories and pictures.

Eden Island Hurghada Booking – Your Complete Guide to Paradise with HurghadaToGo
When travelers think of Hurghada, the Red Sea instantly comes to mind — crystal-clear waters, coral reefs bursting with color, and golden beaches stretching endlessly. Among the many excursions available, Eden Island Hurghada stands out as one of the most exclusive and luxurious experiences.
If you are looking for a way to combine relaxation, luxury, and natural beauty, then Eden Island Hurghada booking through HurghadaToGo is your key to paradise. This long-form guide will cover everything you need to know: the history of Eden Island, what makes it special, the full itinerary, tips for families and couples, practical booking details, and why HurghadaToGo is your best partner for this unforgettable trip.
1. Introduction to Eden Island Hurghada
Eden Island is a private paradise located just off the coast of Hurghada in the Red Sea. It has quickly become one of the most sought-after destinations for day trips in Egypt. Unlike the more crowded public beaches or larger islands, Eden offers exclusivity, tranquility, and a touch of luxury.
From the moment you step onto its soft sandy beach, you feel like you’ve entered another world — where turquoise waters meet lush palm umbrellas, and where time slows down so you can savor every moment.
For tourists searching online, the phrase “Eden Island Hurghada booking” is becoming increasingly popular, as more visitors discover this hidden gem and want a simple, reliable way to reserve their place.
2. Why Choose Eden Island Over Other Islands in Hurghada?
Hurghada offers many day trips to islands such as Giftun, Mahmya, Orange Bay, and Paradise Island. But Eden Island has a unique charm that sets it apart:
- Exclusivity: Fewer visitors mean less crowding and a more private experience.
- Luxury Setting: Designed to feel like a tropical retreat, Eden Island is perfect for those who enjoy comfort and style.
- Natural Beauty: With shallow turquoise lagoons and rich coral reefs, it’s ideal for snorkeling and swimming.
- Relaxation: The focus is on peace and comfort rather than mass tourism.
If you’re the kind of traveler who values quality over quantity, then Eden Island Hurghada booking is the right choice.
3. The Complete Eden Island Hurghada Booking Itinerary
When booking with HurghadaToGo, your day is carefully planned to provide the perfect balance of adventure and relaxation. Here’s what you can expect:
3.1 Pickup from Your Hotel
Your journey begins with a comfortable air-conditioned transfer from your hotel in Hurghada, El Gouna, Makadi Bay, or Sahl Hasheesh. No stress, no delays — just a smooth start to your day.
3.2 Boat Ride to Eden Island
After reaching the marina, you’ll board a modern boat that will take you across the Red Sea. The boat ride itself is an experience, offering panoramic views of the coastline.
3.3 Arrival at Eden Island
Stepping onto the soft white sands feels like entering a dream. You’ll be greeted by friendly staff and directed to your reserved spot with sunbeds, shade, and full facilities.
3.4 Snorkeling and Swimming
The waters surrounding Eden Island are a snorkeler’s paradise. Colorful coral reefs, schools of tropical fish, and sometimes even dolphins can be seen. For those who prefer relaxation, the shallow lagoons are perfect for floating peacefully.
3.5 Lunch and Refreshments
Included in your trip is a delicious buffet lunch with local and international dishes, along with soft drinks to keep you refreshed throughout the day.
3.6 Free Time to Relax
After lunch, the rest of the afternoon is yours. Sunbathe, read a book, explore the island, or take more dips into the turquoise waters.
3.7 Return to Hurghada
In the late afternoon, you’ll board the boat for the return journey, followed by a transfer back to your hotel. You’ll carry home not just photos, but lasting memories of paradise.
4. What’s Included in Eden Island Hurghada Booking
When booking with HurghadaToGo, your trip is all-inclusive, meaning you won’t have to worry about hidden costs. The package typically includes:
- ✅ Hotel pickup and drop-off
- ✅ Boat transfers to and from Eden Island
- ✅ Entrance fees to Eden Island
- ✅ Buffet lunch and soft drinks
- ✅ Use of sunbeds and umbrellas
- ✅ Snorkeling opportunities with gear available
Optional extras may include professional photography, alcoholic beverages, or private cabana rentals.
5. Who Is Eden Island Hurghada Perfect For?
Eden Island is versatile, appealing to a wide range of travelers:
- Couples: Looking for a romantic, private beach escape.
- Families: Safe shallow waters and child-friendly facilities.
- Groups of Friends: A fun day of sun, sea, and laughter.
- Solo Travelers: Perfect for relaxing and meeting new people.
No matter your travel style, Eden Island Hurghada booking ensures a tailored experience for everyone.
6. Tips for Making the Most of Your Eden Island Trip
To maximize your experience, consider these tips:
- Book in advance: Spaces are limited due to the island’s exclusivity.
- Bring reef-safe sunscreen: Protect both your skin and the marine life.
- Carry snorkeling gear if you prefer your own: Though equipment is often provided, some guests like to bring their own mask and fins.
- Don’t forget your camera: The views are postcard-worthy!
- Travel light: Towels, sunbeds, and food are provided, so just pack essentials.
7. Why Book Eden Island Through HurghadaToGo?
Choosing the right tour agency makes all the difference. Here’s why HurghadaToGo is the best partner for your Eden Island Hurghada booking:
- 🌍 Local Expertise: We know Hurghada and its islands inside out.
- 📞 Easy Communication: Book via WhatsApp, email, or our website.
- 🏆 Trusted Reputation: Hundreds of happy customers recommend us.
- 🚌 Convenience: Comfortable transfers from all major hotels and resorts.
- 💰 Best Value Guarantee: Competitive pricing without compromising quality.
- 🗣️ Multilingual Guides: English, German, French, Russian, and more.
With HurghadaToGo, your experience is stress-free from start to finish.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Eden Island Hurghada Booking
Q: How far is Eden Island from Hurghada?
A: It’s about a 30–45 minute boat ride, depending on the weather.
Q: Is Eden Island suitable for children?
A: Yes, the shallow waters and family-friendly facilities make it perfect for kids.
Q: Can I book Eden Island privately?
A: Yes, HurghadaToGo can arrange private bookings for special occasions or VIP experiences.
Q: What should I bring with me?
A: Sunglasses, sunscreen, swimwear, and a camera. Everything else is provided.
Q: How do I confirm my Eden Island Hurghada booking?
A: Simply contact HurghadaToGo via WhatsApp (+201009255585), email ([email protected]), or through our website.
9. How to Book Eden Island Hurghada with HurghadaToGo
Making a reservation is simple:
- Visit our website: HurghadaToGo.com
- Send us a WhatsApp message: +201009255585
- Email us at: [email protected]
Provide your name, hotel, preferred date, and number of guests — we’ll confirm your Eden Island Hurghada booking instantly.
10. Conclusion – Book Your Slice of Paradise Today
Eden Island isn’t just another excursion in Hurghada — it’s an experience of luxury, exclusivity, and natural beauty. Whether you’re traveling as a couple, a family, or a group of friends, Eden Island Hurghada booking with HurghadaToGo ensures a smooth, stress-free, and unforgettable day in paradise.
Don’t wait until the last minute. Book today and secure your place in one of Hurghada’s most beautiful escapes.
📍 Book now with HurghadaToGo – Your trusted partner for Red Sea adventures.